Introduction
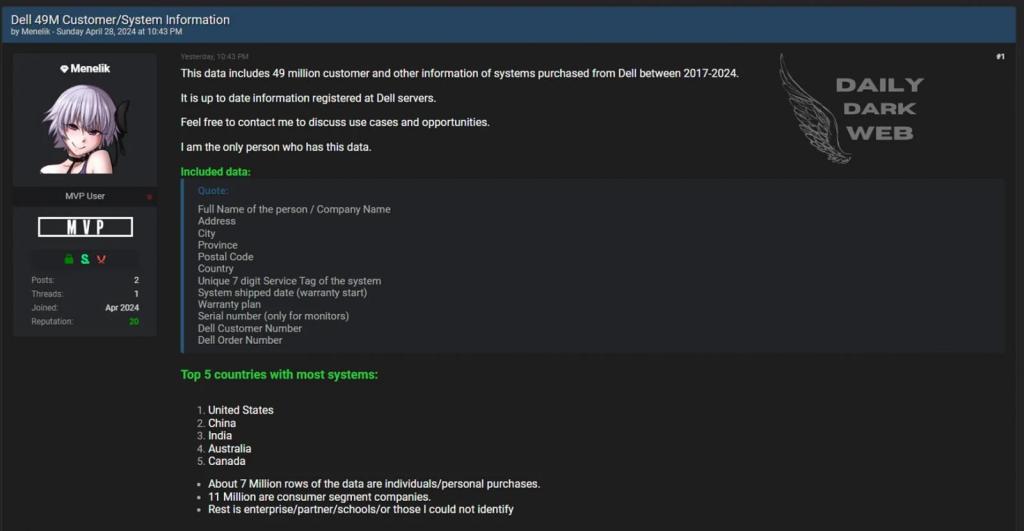
On July 4, 2024, the cybersecurity community was rocked by the discovery of RockYou2024, the largest password compilation leak in history. This staggering breach, revealed by a Cybernews research team, includes nearly 10 billion unique plaintext passwords. The massive dataset, posted on a popular hacking forum, presents severe security risks, especially for users prone to reusing passwords.
The RockYou2024 Password Leak
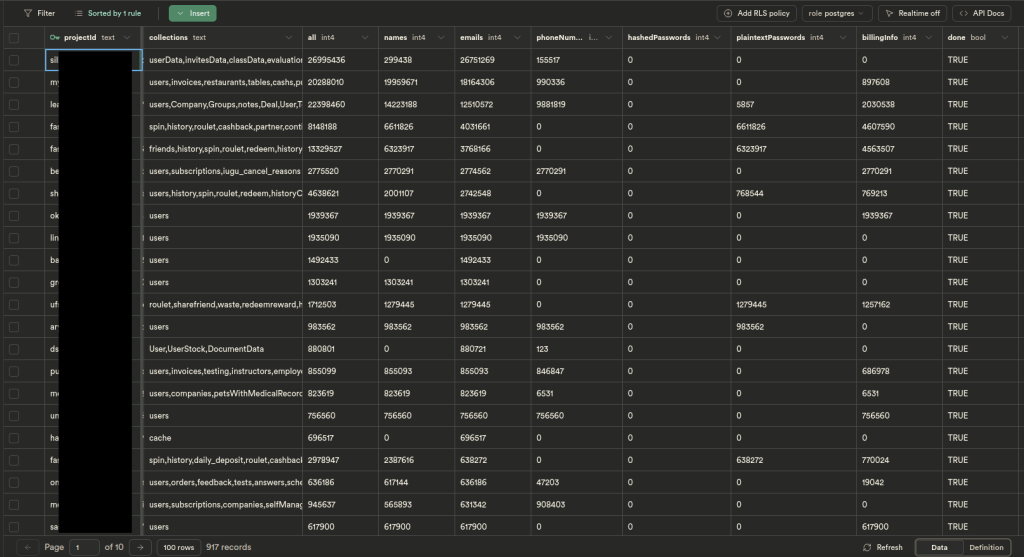
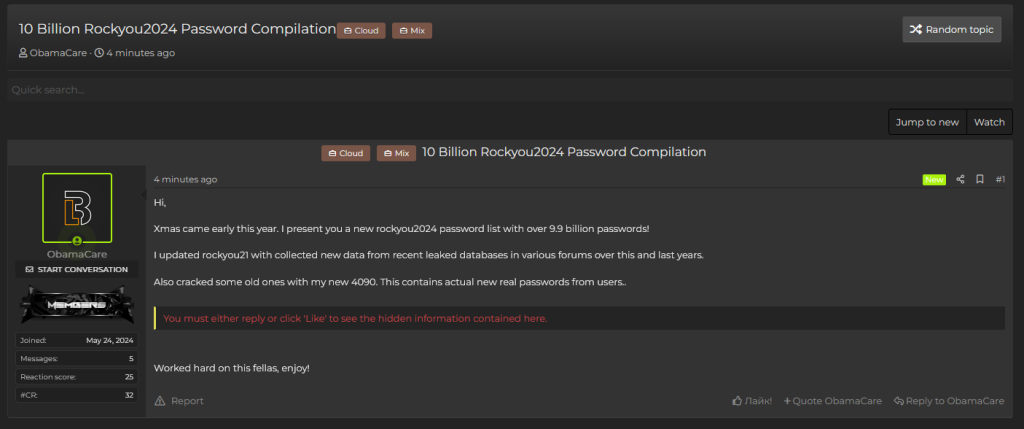
The RockYou2024 password leak, tracked as the largest of its kind, was unveiled by Cybernews researchers. The file, named rockyou2024.txt, contains an astounding 9,948,575,739 unique plaintext passwords. The dataset was posted by a user named “ObamaCare,” who has a history of leaking sensitive information. This compilation is believed to be a mix of old and new data breaches, significantly increasing the risk of credential stuffing attacks.
A Brief History of RockYou
The RockYou series of password leaks dates back to 2009, when the original RockYou breach exposed over 32 million user account details. In 2021, the RockYou2021 compilation, containing 8.4 billion passwords, set a new record at the time. RockYou2024 expands on this legacy, adding another 1.5 billion new passwords, making it the largest password dump to date.
Impact and Exploitation Risks
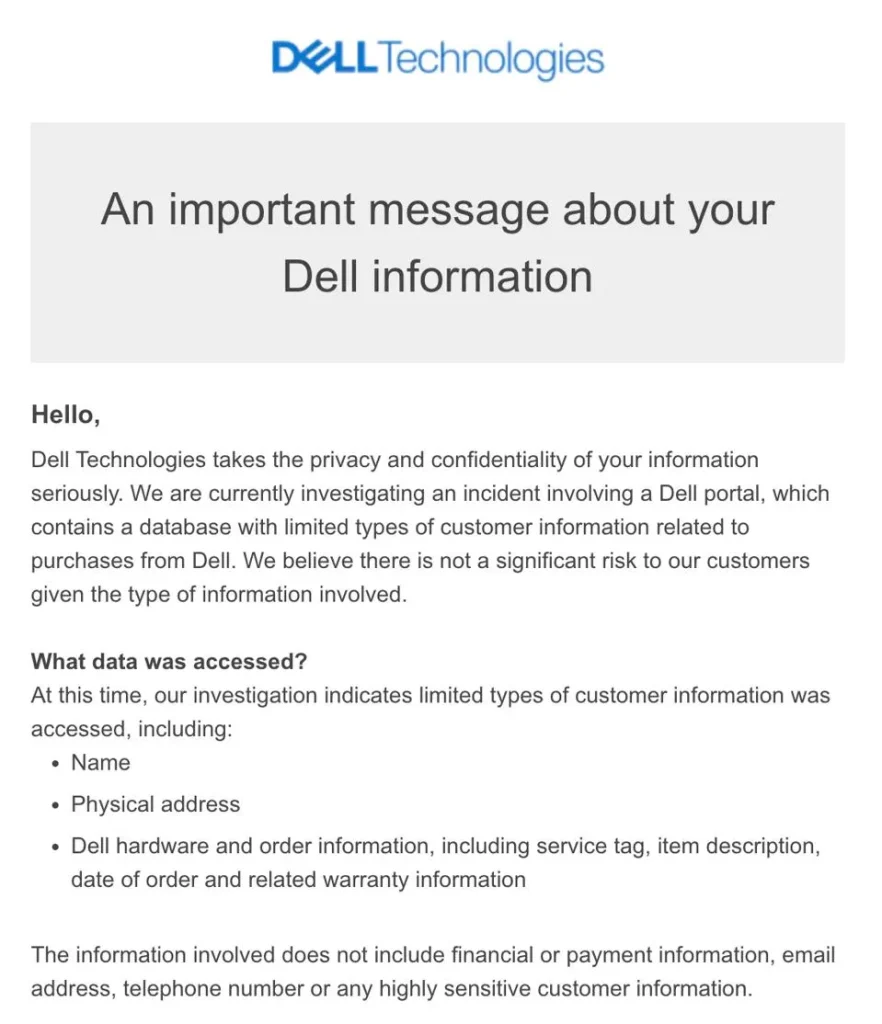
The RockYou2024 leak poses significant dangers due to the vast number of real-world passwords it contains. Cyber-criminals can leverage this data to execute brute-force attacks, attempting to gain unauthorised access to various online accounts. Combined with other leaked databases containing usernames and email addresses, RockYou2024 could lead to widespread data breaches, financial fraud, and identity theft.
How to Protect Against RockYou2024
Reset Compromised Passwords
Immediately reset passwords for any accounts associated with the leaked data. Ensure new passwords are strong, unique, and not reused across multiple platforms.
Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Enable MFA wherever possible. This adds an extra layer of security by requiring additional verification beyond just a password.
Implement Passwordless Solutions
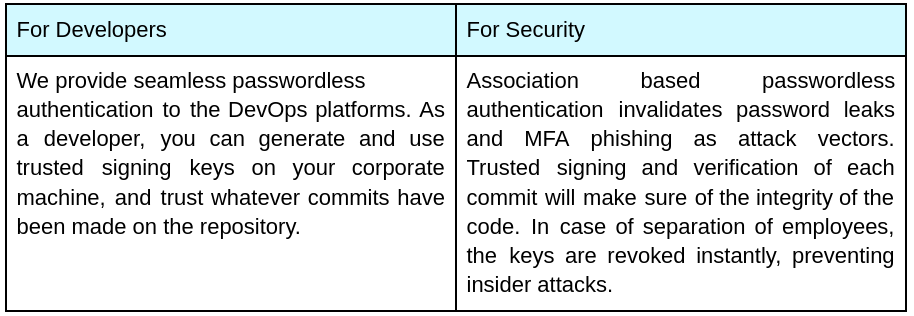
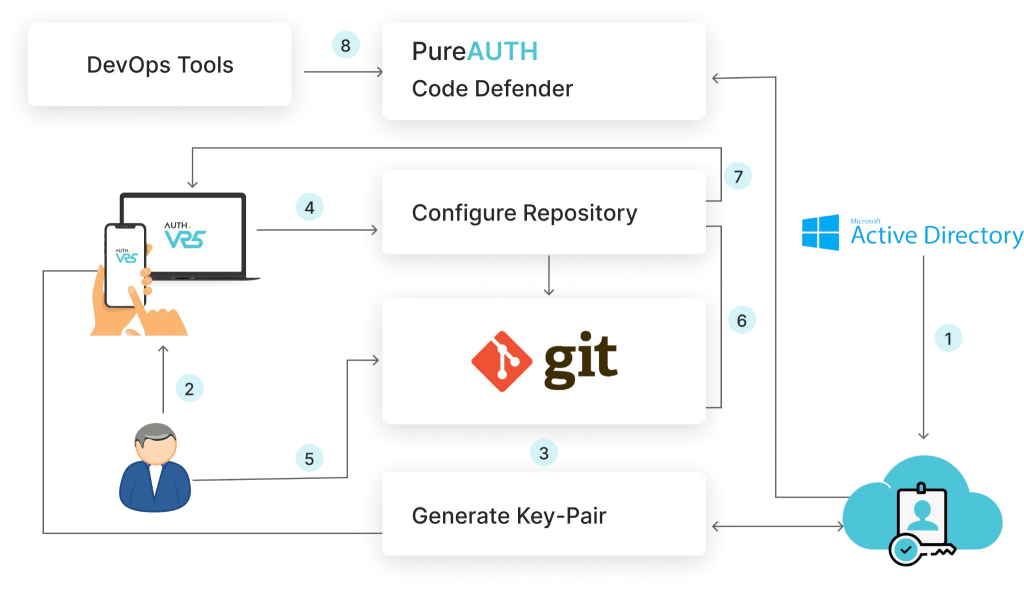
Adopting passwordless solutions can further enhance security. SAML-based passwordless solutions, such as Single Sign-On (SSO) systems, eliminate the need for passwords by using secure tokens for authentication. These solutions reduce the risk of password-related attacks and improve user convenience.
Monitor Accounts and Stay Informed
Regularly monitor accounts for suspicious activity and stay informed about the latest cybersecurity threats and best practices.
Conclusion
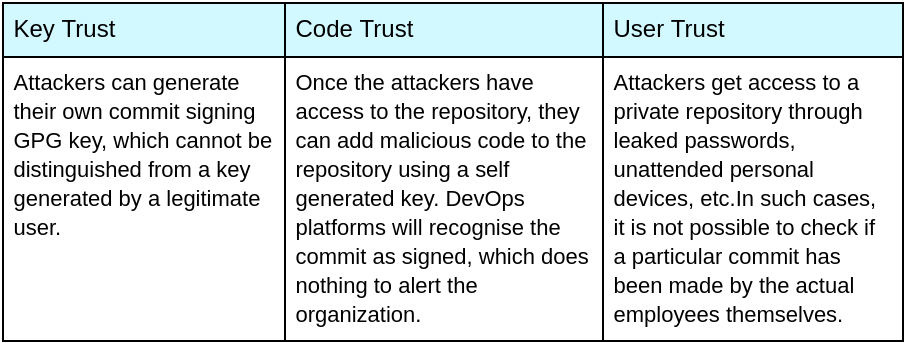
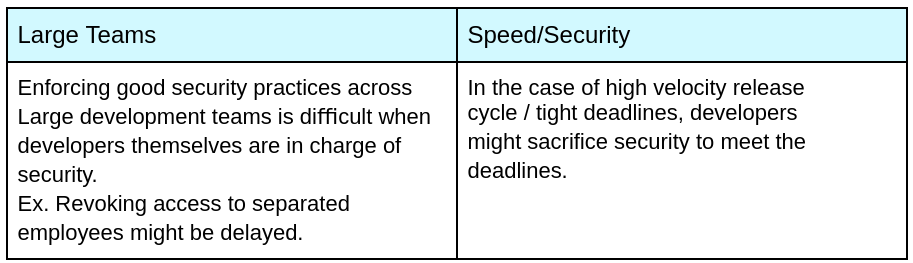
This recent breach highlights how fragile and unsafe passwords are, underscoring the need for more secure authentication methods. The RockYou2024 leak demonstrates that even with strong, unique passwords, the risks remain significant. Multi-factor authentication (MFA), while an added layer of security, is not foolproof. For example, MFA breaches such as the 2022 Uber hack and the attack on Microsoft’s Office 365 users in 2021 show its vulnerabilities.
Additionally, password managers are not entirely reliable. The Okta breach in 2022 and the OneLogin breach in 2017 exposed millions of user accounts, demonstrating that even these tools can be compromised.
In light of these risks, passwordless systems are emerging as the next hot trend in cybersecurity. SAML-based passwordless solutions, like PureAuth, provide enhanced security by eliminating the need for passwords and reducing the attack surface for cybercriminals.
Embracing passwordless systems, combined with continuous monitoring and updated security practices, is essential for protecting against the evolving threat landscape. Stay ahead of cyber threats by adopting innovative authentication methods and ensuring your digital assets are well-protected.