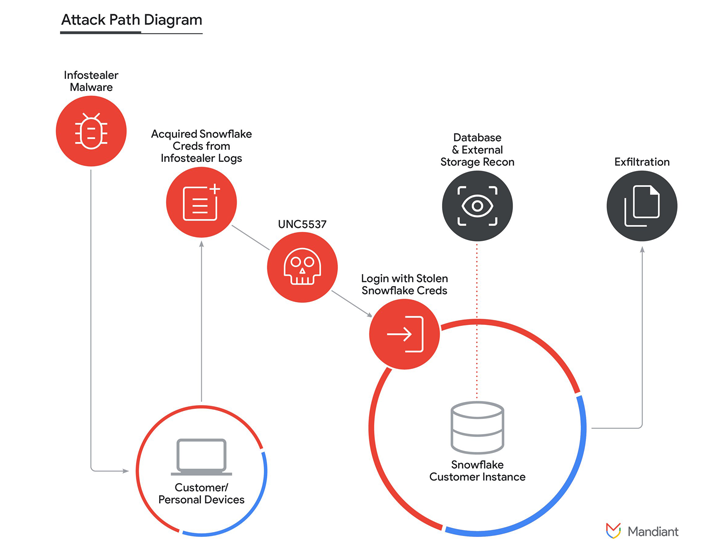
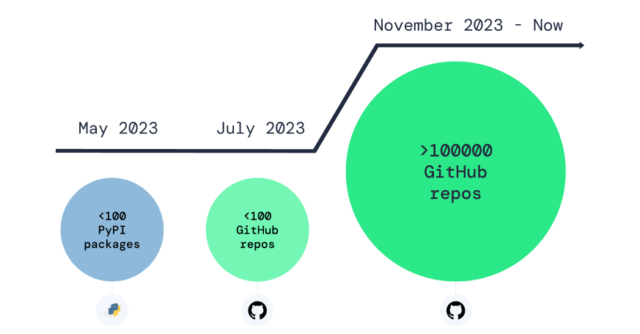
Introduction
The New York Times recently experienced a significant security breach, leading to the leak of their source code. This breach was initiated through an exposed GitHub token, allowing unauthorised access to their repositories
How It Happened
An anonymous hacker posted the New York Times’ source code on 4chan. The breach occurred due to an exposed GitHub token, which provided access to over 5,000 repositories, totalling 270 GB of data. The stolen data included sensitive and proprietary information.
Response from The New York Times
The New York Times confirmed the breach and revealed that a credential was inadvertently exposed in January 2024. They quickly addressed the issue, emphasising that their systems remained non-compromised and their operations unaffected. However, this incident highlights the critical need for stringent security measures.
Implications of the Leak
The breach exposed vast amounts of data, including source code for various projects. This poses significant risks for the New York Times, including potential security vulnerabilities and intellectual property theft. The leaked data also included uncompressed tar files, with the hacker urging users to seed due to potentially insufficient seed-boxes. Reactions ranged from disbelief at the volume of repositories to jokes about the newspaper’s digital complexity.
Connection to Disney Leak
Just days before, another breach occurred involving Disney’s internal servers. A hacker associated with the defunct game Club Penguin leaked 2.5 GB of sensitive data, including corporate strategies and internal emails. This shows a disturbing trend of high-profile data breaches. The Disney breach exploited Confluence servers via exposed credentials, further emphasising the need for robust security practices.
Conclusion
This incident underscores the critical importance of securing access tokens and implementing robust security measures to prevent unauthorised access to sensitive information. As cyber threats evolve, organizations must remain vigilant and proactive in safeguarding their digital assets. Securing the CI/CD Pipeline should be a priority for every organization and PureID’s CASPR can be a game-changer.