Cisco recently issued a warning about large-scale brute-force attacks targeting VPN and SSH services on Cisco and other devices worldwide. These attacks pose significant risks to enterprise security, necessitating immediate action.

Cisco Warning and Compromised Services
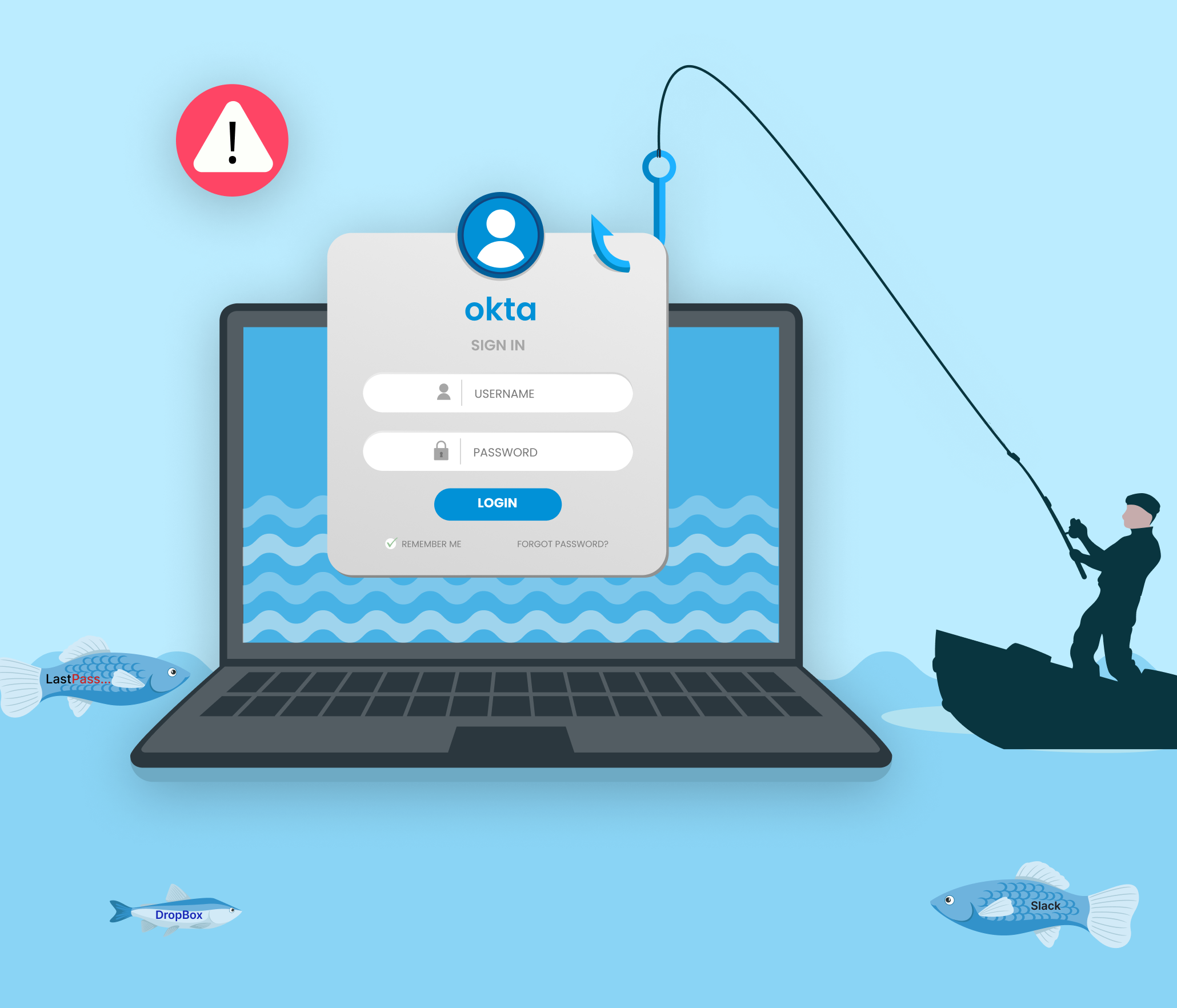
Cisco Talos reports a surge in brute force attacks since March 18, 2024, targeting VPN services. These assaults exploit vulnerabilities in traditional password-based authentication, compromising network integrity. The known affected services are following:
- Cisco Secure Firewall VPN
- Checkpoint VPN
- Fortinet VPN
- SonicWall VPN
- RD Web Services
- Miktrotik
- Draytek
- Ubiquiti
History: Not so Private Virtual Private Networks
If you are here reading this blog, you know the drill. Maybe a password is slipped in code, spoofed, phished, whaled, 2FA or MFA is breached, or even a vendor is breached, and your organization and user information lies in the hands of a threat actor. According to an HBR Report “The FBI regards a cybersecurity breach at every organization—including yours—as a matter not of ‘if,’ or even ‘when,’ but ‘how often.'”
Most often then not, these threat actors will siege your assets, ask for ransom and cause a lot of trouble. Two out of Three organizations, without a regard of size, have faced ransomware in 2023. Beyond the cost of expenses, including, potentially, the ransom itself, downtime averages $365,000 an hour in revenue loss. When you consider that the average recovery time is three weeks, it becomes clear how devastating these attacks can be.
In our previous blog we have discussed VPN breaches in detail. Anyhow, here’s some compact data for you.
| Affected Entity | Root Cause | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Avast Antivirus | Stolen credentials | Adversaries modified the CCleaner distributed by Avast . |
| Lockheed Martin | CVE-2011-0609 | Critical data related to the defence contracts leaked. |
| Pulse Secure | CVE-2019-11510 | 1000 enterprises are at risk of ransomware attacks. |
| Ukraine Power grid | Malware | Power grid taken offline leading to no electricity for thousands. |
Brute Force Attacks
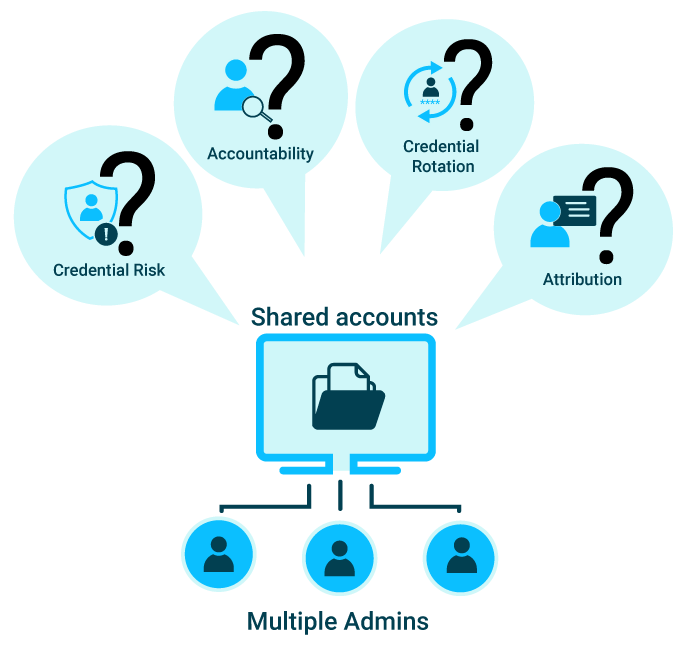
Brute force attacks involve systematically trying multiple username-password combinations until the correct one is found. Attackers leverage proxies like TOR, VPN Gate, IPIDEA Proxy etc to conceal their origins, intensifying the challenge of detection.Password spray attacks, on the other hand, target numerous accounts with commonly used passwords, increasing the likelihood of success.
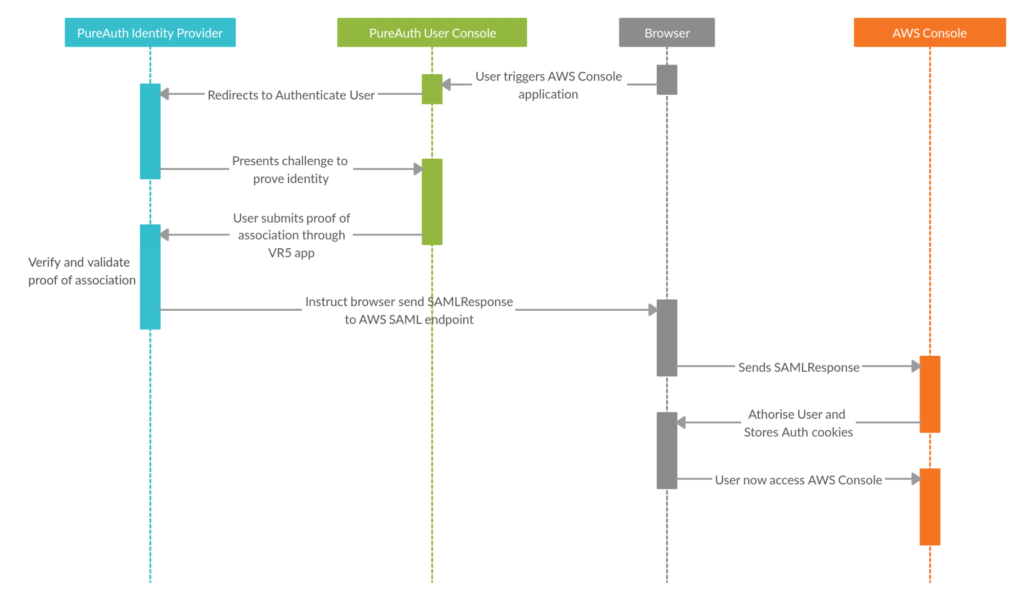
Your Knight in Passwordless Armour – PureAuth
In light of escalating threats, enterprises must prioritise the adoption of passwordless VPN solutions. Embracing innovative authentication mechanisms ensures a resilient defence against evolving cyber threats.

Transitioning to passwordless VPN systems offers a robust defence against brute force attacks. By eliminating passwords, these systems thwart credential stuffing attempts, enhancing overall security.
Conclusion
In the face of mounting VPN vulnerabilities, the imperative to transition to passwordless systems cannot be overstated. By embracing advanced authentication methods, organisations can fortify their defences against brute force attacks, safeguarding critical assets and data.
Read Also
Your 1st Step to #GoPasswordless
Credential stuffing Attacks on VPN: Serious Risk for Enterprise