Abstract
In a recent revelation, Cloudflare disclosed a security breach on Thanksgiving Day, November 23, 2023. This blog delves into the timeline of events and emphasises the critical role of passwordless authentication in mitigating such breaches.
Breach Overview: Understanding the Thanksgiving Intrusion
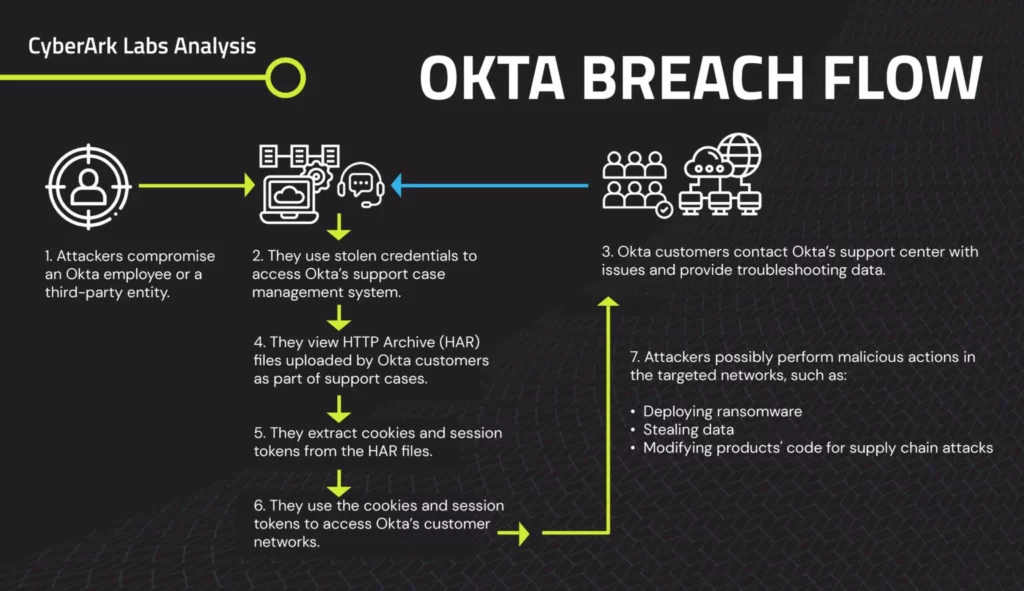
In an orchestrated attack, threat actors exploited stolen credentials from the Okta security breach in October. Cloudflare’s internal systems, particularly the Atlassian server, became the focal point for unauthorised access and data compromise.
Compromised Credentials: The Fallout on Cloudflare’s Security
Despite the awareness of the Okta breach, Cloudflare’s failure to rotate service tokens that have very long validity and account credentials allowed threat actors to establish persistent access. This breach impacted Cloudflare’s Atlassian environment, leading to unauthorised access to sensitive documentation and a limited set of source code repositories.
Nation-State Attribution and the Real Culprit: Passwords
Cloudflare attributes the breach to a likely nation-state actor, mirroring the recent trend in cyber threats. However, one can suggest that the fundamental issue lies in the continued reliance on a vulnerable authentication method, which enables such breaches to unfold.
Highlighting the Key Issue: The Perils of Passwords
The breach underscores the inherent vulnerability of conventional password systems. Stolen Okta credentials served as the gateway for threat actors, exposing the limitations of password-centric security measures. This incident highlights the urgent need for organisations to transition towards passwordless authentication solutions & short session validity to fortify their security posture.
It’s the painful experience of passwords based login which forces admins and users to choose long term session tokens to minimise the number of logins.
PureID Solution: A Glimpse into a Secure Future
PureID offers a robust passwordless authentication solution that would have mitigated this breach. By eliminating the relevance of stolen credentials, PureID represents a paradigm shift in cybersecurity, providing a secure alternative to traditional password systems.
PureAUTH offers a simple & smooth login experience. This makes working with short term sessions and frequent login delightful.
Risk Mitigation: The Imperative of Passwordless Security
Cloudflare’s breach serves as a wake-up call for organizations to reevaluate their cybersecurity strategies. Embracing passwordless solutions, such as PureID, emerges as a proactive step to mitigate the risks associated with stolen credentials and enhance overall security.
Immediate Response: Cloudflare’s Security Reinforcement
In response to the breach, Cloudflare has initiated a comprehensive security reinforcement effort. Measures include mass credential rotation, system segmentation, forensic triage, and a meticulous review of all systems to ensure the threat actor’s access is fully revoked.
Ongoing Investigation: Collaboration for a Secure Future
Cloudflare’s ongoing collaboration with peers, law enforcement, and regulators emphasises dedication to assessing the breach’s full impact. This collaborative approach aims to implement additional preventive measures and adapt to the evolving landscape of cyber threats.
Conclusion: Advocating for Passwordless Security
The Cloudflare breach underscores the critical need to shift from traditional passwords and false passwordless systems to true passwordless authentication that can not be breached by stolen credentials. Passwordless solutions, like PureID, offer a robust defence against unauthorised access, heralding a more secure digital future for organisations.