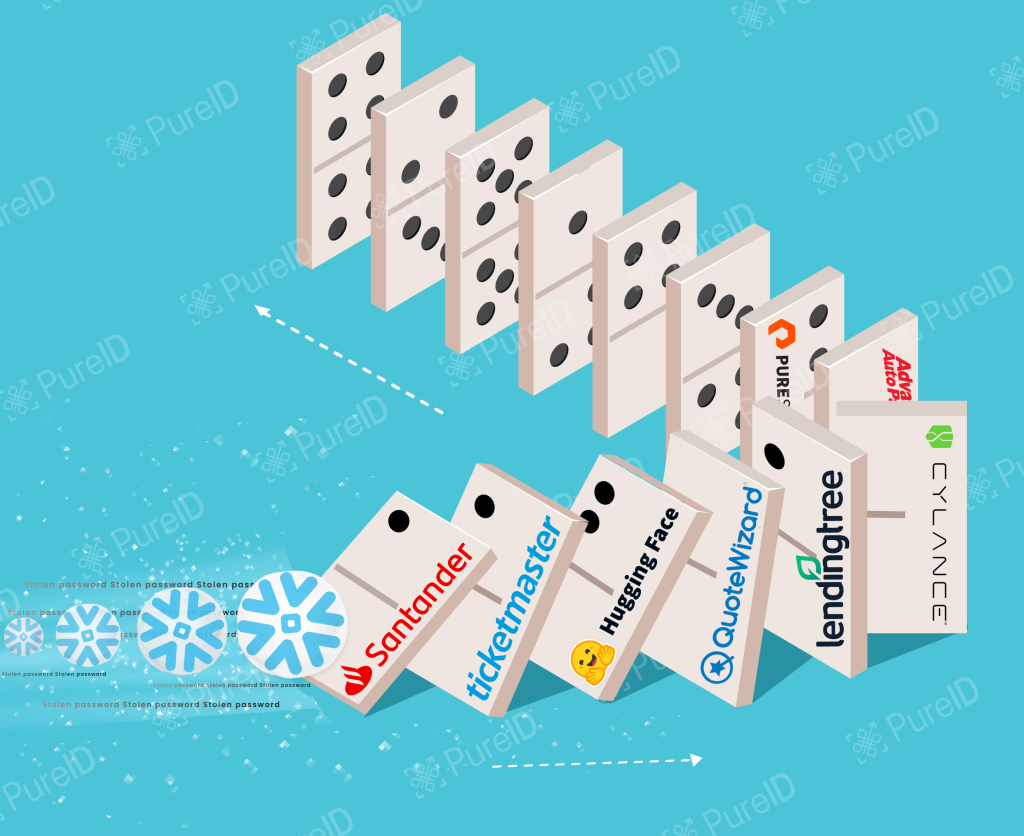
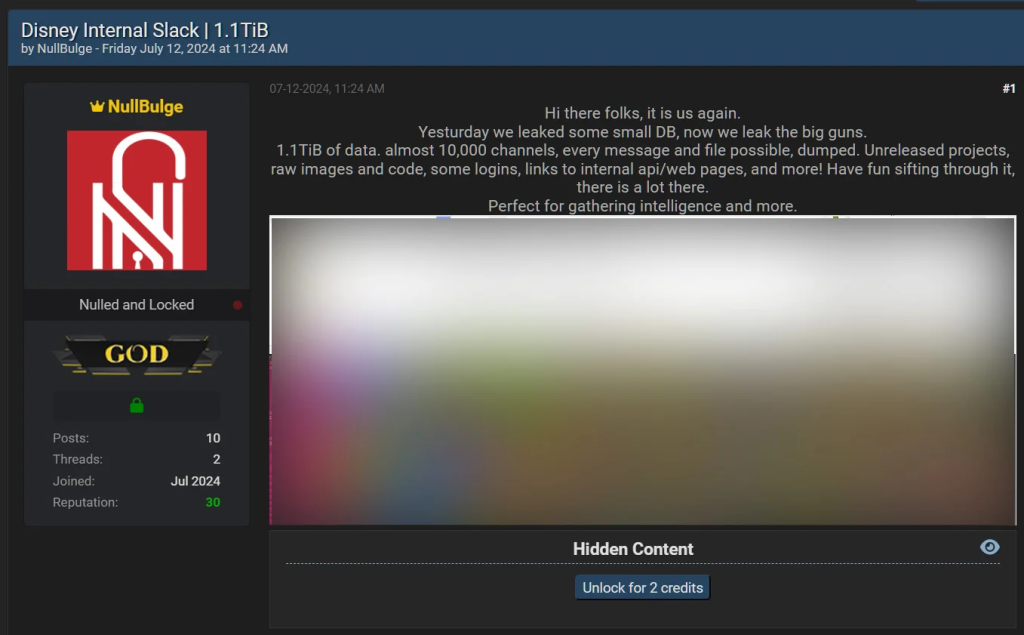
Walt Disney Co. is transitioning away from Slack after a serious data breach. The breach, which occurred in July 2024, compromised more than 1.1 terabytes of confidential data. This incident included 44 million messages and inside information about various projects at Slack. According to a news article in The Wall Street Journal, Disney has decided to shift to new corporate-wide communication software before the end of its fiscal year.

Why Disney Is Getting Off Slack
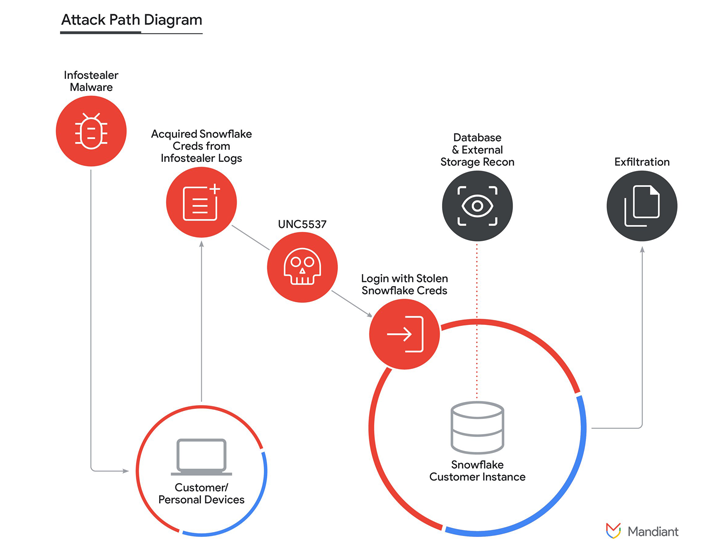
The NullBulge hack led Disney to move away from Slack. Hackers accessed thousands of internal channels, exposing unreleased projects, login credentials, and sensitive corporate data. This breach highlighted Slack’s vulnerability, especially due to weak employee security practices like not using robust authentication.
Disney’s decision isn’t just a reaction to the breach but a preventive step to reduce reliance on a platform that became a weak link in its cybersecurity. By switching to streamlined collaboration tools, Disney aims for platforms that offer tighter security and better integration with its IT systems.
History of Breaches at Disney
This is not the first time that the House of Mouse has faced a breach. In July 2024, Disney suffered a breach that exposed over 1.1TB of sensitive data, including 44 million messages, 18,800 spreadsheets, and internal project details. Several months ago in early June 2024, hackers targeted the Club Penguin Confluence server and led to leaking of 2.5 GB of data and information related to the company’s legacy operations.
Mitigation and Prevention: Enhancing Your Security Position
To prevent future incidents, companies like Disney harden up their security approach. One of these approaches involves using zero-trust products, where all actions are considered to be malicious unless proved otherwise and authenticated. The shift away from Slack for Disney should be used as an opportunity to have stronger encryption and more secure, decentralised methods of communication in a place.
Despite the risks, companies often prioritise familiar tools like Slack for their ease of use. Employees enjoy the convenience of SSO and real-time communication. However, this same ease of use can make these platforms vulnerable to attacks, as Disney’s breach demonstrated. Companies often avoid stricter security measures, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), due to perceived inconvenience. This balance between convenience and security is where many organizations falter.
PureAUTH on the other hand, offers one-click access through passwordless authentication, which is friendly and secure.
Conclusion : One Move Toward Collaboration Over A Secure Platform
As Disney steps away from Slack, this highlights an emerging trend: companies must prioritise security in their collaboration tools. Convenience is awesome, but so is the robust security against emerging threats. PureAUTH balances convenience with the protection required to secure company data. If Disney had solutions like PureAUTH, then the breach might have been far less effective. As companies rethink their internal platforms for communication, the lesson is stark: security and usability are not mutually exclusive with PureAUTH. #gopasswordless